chapter 3 power point.pptc ccvcvvscscddcd
- 1. Chapter 3 structure and function of cells Mabast M. Ahmed
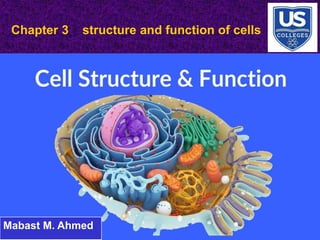
- 2. Chapter 3 structure and function of cell Contents 3-1 introduction to the cell 3-2 parts of the eukaryotic cell 3-3 multicellular organization
- 3. Objectives of this section Outline the discoveries that lead to the development of cell theory State the cell theory and their types Identify a limiting factor affect on the size of cells . Describing the relationship between cell shape and cell function . Differentiate between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. section 3-1 Structure and functions of the cell
- 4. Discovery of the cell • The discovery of cells was made by development of the microscope. • Robert Hooke • Was first scientist who used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork (dead plant cell). • He wrote: “I could exceedingly plainly perceive it to be all perforated and porous,” and he further described it as consisting of “a great many little boxes”, these “little boxes” reminded him of the small room in which monks lived, so he called them cell. • Anton van Leeuwenhoek • Was first person to observe living cells. Section 1 Introduction of the cell Chapter 3
- 5. A short video about cell discovery
- 6. The Cell Theory The Cell Theory has three parts: 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. Chapter 3 Section 1 Introduction of the cell
- 7. • Mattias Schleiden • He concluded that all plants are composed of cells. • Theodor Schwann • He concluded that all animals are composed of cells. • Rudolf Virchow • He reasoned that cells come only from other cells. Section 1 Introduction of the cell Chapter 3
- 8. The Diversity • Not all cells are alike. Cells have different size, shape & internal organization. • Our bodies contain at least 200 different cell types • Cell Size » Most plant and animal cells have a size between (10 _ 50 ) micrometer Some Bacterial cells are only 0,2 micrometer Most cells are visible only with aid of microscope • Cells are limited in size by ratio between surface area and volume. » For a cuboidal cell: • Volume increases with the cube of the side length, but surface area increases with the square of the side length. This means: (if a cell keeps the same shape as it grows, its volume will increase more rapidly than its surface area. • This trend is important because the materials needed by a cell (such as nutrients and oxygen) and the wastes produced by a cell (such as CO2) must pass into and out of the cell through its surface. Chapter 3 Section 1 Introduction of the cell
- 9. V = length X width X height S.A. = length X width X n.s
- 10. Cell shape Cells come in a variety of shapes, such as: • Nerve cell: The long extensions that reach out in various directions from the nerve cell, allow the cell to send and receive nerve impulses. • Skin cell: The flat shape of dead skin cells is well suited to their function of covering and protecting the body surface. • White blood cell (WBC): can change shape, leave the blood, and enter the areas surrounding blood vessels. This allows them to move through narrow openings and to isolate, engulf, and destroy bacteria that invade the body Chapter 3 Section 1 Introduction of the cell
- 11. Cell shape
- 12. • Internal Organization • Cells contain a variety of internal structures called: Organelles. • Organelle: is a cell component that performs specific functions for the cell. • Cell membrane: is the thin membrane that surround entire cell. – most of the organelles are surrounded by their own membranes. • Nucleus: is the large organelle near the center of the cell, that contains genetic information and directs most of the activities of cell. Chapter 3 Section 1 Introduction of the cell
- 14. • Types of cell (depend on membrane bound nucleus) • Eukaryotic cell: is a cell that have a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles – Such as: human cell, animal cell, plant cell. • Prokaryotic cell: is a cell that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. – Such as: bacteria cell. Chapter 3 Section 1 Introduction of the cell
- 15. Main components of Eukaryotic cell: 1.Cell membrane 2. Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm Section 2 Parts of Eukaryotic Cell Chapter 3
- 16. The Cell Membrane • Definition: is a selectively permeable barrier that let some substances easily cross to inside of cell, while others cannot cross at all. • Composition: it is made primarily of: • Lipids and proteins. Section 2 Cell Parts Chapter 3
- 17. Membrane Lipids: • Phospholipid: – is one of the major types of lipids in the cell membranes, which is bilayer. – Has: • Polar head: points outward, is (hydrophilic), (water loving) • Nonpolar tail: is confirmed to the interior of the cell membrane, is (hydrophobic), (water fearing) • Steroid: – is another type of lipid, which fits between the tails of the phospholipids. • The major membrane steroid in animal cells is (Cholesterol). • Other steroids are found in the cell membranes of plant. Section 2 Cell Parts Chapter 3
- 20. Lipid Bilayer Section 2 Cell Features Chapter 3
- 21. Phospholipid Section 2 Cell Features Chapter 3
- 22. A video about phospholipid bilayer
- 23. Membrane Proteins: • Peripheral proteins: – Definition: are proteins that attached to the surfaces (outside & inside) of the cell membrane. • It can link by weak bond with the “membrane lipids” or to “other proteins” that are embedded in the lipid bilayer. • Integral proteins: – Definition: are proteins that embedded in the bilayer. • Some are extend across the entire cell membrane and are exposed to both the inside and the exterior environment. • Others extend either only to the inside or only to the exterior surface. Section 2 Cell Parts Chapter 3
- 24. Membrane Proteins: • Carbohydrates • integral proteins exposed to the cell’s external environment often have carbohydrates attached. • Function: – They may hold adjoining cells together – They may act as sites where viruses or chemical messengers such as hormones can attach. • Functions of Membrane proteins: – play an important role for transporting molecules through lipid bilayer, such as: • Some integral proteins form channels or pores through which certain substances can pass. • Other integral proteins can bind to a substance on one side of the cell membrane and carry it to the other side of the membrane. Section 2 Cell Parts Chapter 3
- 25. Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane – Scientist have discovered that cell membranes are very dynamic. • The fluid mosaic model states that the lipid bilayer behaves like a fluid more than it behaves like a solid. • Because of this fluidity, the membrane’s lipids and proteins can move laterally within the lipid bilayer, and their patterns in cell membrane are constantly changing. Section 2 Cell Parts Chapter 3
- 27. Organelles • Cytoplasm – Definition: is the fluids and cell organelles inside the cell, located between cell membrane and nucleus. • Cytosol – Definition: is the gelatin like aqueous fluid, in which salts, minerals and organic molecules are dissolved. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 29. Mitochondria – Definition: are large organelles, and are the sites of chemical reactions that transfer energy from organic compounds to ATP. • Specialties: – They are usually more numerous in cells that have a high energy requirement. For example: » Liver cells: each contain as many as 2,500 mitochondria. » Muscle cells: contain many mitochondria. – Mitochondrion is surrounded by 2 membranes: • Smooth outer membrane: serve as a boundary between the mitochondrion and the cytosol. • Inner membrane: has many long folds, known as cristae. » Cristae: enlarge the surface area of the inner membrane, providing more space for the chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondrion. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 31. Ribosomes • Definition: are the most numerous organelles in many cells, and play an important roles in the synthesis of proteins. • Specialties: – They are not surround by a membrane. – They are an assemblage (collection) of 2 organic compounds: protein & RNA. – They are packaged inside the nucleus, then transported to cytosol. – Some of them remain free within the cytosol, while others become attached to an organelle called: endoplasmic reticulum. – play an important roles in the synthesis of proteins; » Proteins to be used within the cytosol are produced on the ribosomes that are free in the cytosol. » Proteins to be inserted into membrane or exported from cell, are produced on the ribosomes that are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 32. Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 33. Endoplasmic Reticulum • Is abbreviated “ER” • Definition: is a system of membranous tubules and sacs. • Function: act as an intracellular highway, a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another. • Types: – Rough ER: is covered by ribosomes which give the ER rough appearance. » is prominent in cells that make large amounts of proteins to be exported from the cell or inserted into cell membrane. – Smooth ER: is not covered by ribosomes, and is involved in the: » Synthesis of steroids in gland cells. » Regulation of calcium levels in muscle cells. » Breakdown of toxic substances by liver cells. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 35. Golgi Apparatus • Definition: is the processing, packaging, and secreting organelle of the cell, and is a system of membranes. • Appearance: appears as a series of flattened sacs with a characteristic convex shape in the cytosol. • Function: is working with “ER”, which modifies proteins for export by the cell. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 36. Lysosomes • Definition: are small, spherical organelles that enclose hydrolytic enzymes within single membrane. – They are common in the cells of animals, fungi & protists, but they are rare in plant cells. • Function: • Can digest protein, carbohydrates, lipids, DNA & RNA. • They may also digest old organelles, viruses & bacteria that have been ingested by a cell. • In some multicellular organisms, play a role during early development, for example: » The human hand begins as a solid structure in the embryo. As the embryo develops, lysosomal enzymes selectively destroy tissue to form the spaces between the fingers. Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 37. Cytoskeleton • Definition: is a network of protein strands, that not surrounded by membranes. • Function: • maintain shape and size of cell • Participates in the movement of organelles within the cytosol. • Types: – microfilaments: are threads made of a protein called actin. And is the smallest strands that make up the cytoskeleton. • Function: – They contribute to cell movement. – Play role in the muscle cell contraction. – microtubules: are hollow tubes, and are the largest strands of the cytoskeleton. • Function: – When a cell is about to divide, bundles of microtubules (spindle fibers) come together and extend across the cell. – Spindle fibers assist in movement of chromosomes during cell division Section 2 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 40. Cilia and flagella • Cilia and flagella:- are hairlike organelles that extend from the surface of the cell . They assist in movement. Cilia and flagella can be found in many eukaryotic cells . When these organelles are short and present in large number , they are called cilia . Cilia in unicellular organisms aids in : Search for food Escape from predator Cilia also found in multicellular organisms in the cells that lining your respiratory tract . When the hairlike organelles are long and less numerous on a cell , they are called flagella . Example : sperm cells that have only one flagella .
- 41. Structure of Cilia and Flagella Section 2 Cell Features Chapter 3
- 42. The Nucleus • The nucleus is an internal compartment that houses the cell’s DNA. Most functions of a eukaryotic cell are controlled by the cell’s nucleus. • The shape of nucleus are maintains with the help of protein skeleton known as nuclear matrix • The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. • Inside nuclear envelope are fine strand known as chromatin. Chromatin is a combination of DNA and protein. During cell division the chromatin strands coil up and condensed to form chromosomes . Scattered over the surface of the nuclear envelope are many small channels called nuclear pores. Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 43. The Nucleus, continued Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 44. The Nucleus , continuous functions of nucleus :- 1) Storing hereditary information in DNA. 2) Act as a side where RNA is copied from DNA 3) Direct synthesize of protein by producing ribosome in nucleolus. Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 45. Nucleus of a Cell Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 46. Structures of Plant Cells Plants have three unique structures that are not found in animal cells: • Cell Wall • Chloroplasts • Central Vacuole Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 47. Parts of a Plant Cell Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 48. Structures of Plant Cells, continued • The cell membrane of plant cells is surrounded by a thick cell wall, composed of proteins and carbohydrates. • Cell wall are two types : 1. Primary cell wall :- develops during plant cell forming 2. Secondary cell wall :- forms when a cell reaches the full size secondary cell wall develops between primary cell wall and cell membrane. The cell wall helps support and maintain the shape of the cell protects the cell from damage connects the cell with adjacent cells Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 49. Parts of a Cell Wall Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 50. Structures of Plant Cells, continued Central Vacuole: • Most of a plant cell’s volume is taken up by a large, membrane-bound space called the central vacuole. • The central vacuole stores water and may contain enzymes , ions, nutrients, and wastes such as toxics Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 51. Vacuoles Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 52. Plastids • Plastids:- are organelle that surrounded by two membrane and contain DNA. Function : store starch or fat and contain pigments which absorb visible light. The most familiar type of plastids is chloroplast Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 53. Plastids , continuous Chloroplasts are organelles that use light energy to make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. Chloroplast encloses a series of flattened sacs that called thylakoid. • Chloroplasts, along with mitochondria, supply much of the energy needed to power the activities of plant cells. • And contains a large amount of green pigment which gives the leaves their green color • Chloroplasts, like mitochondria, have their own DNA and reproduce independently of the plant cell. • Chloroplasts, like mitochondria, are thought to be descendants of ancient prokaryotes.
- 54. Chloroplasts Section 3 Cell Organelles Chapter 3
- 55. Multiple Choice Use the figure below and your knowledge of science to answer questions 1–3. Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 56. Multiple Choice, continued 1. Which structures in this cell are also found in prokaryotic cells? A. A and B B. C and D C. E and F D. A and E Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 57. Multiple Choice, continued 1. Which structures in this cell are also found in prokaryotic cells? A. A and B B. C and D C. E and F D. A and E Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 58. Multiple Choice, continued 2. Which features of plant cells are missing from this cell? F. cell wall and chloroplasts G. Golgi apparatus and mitochondria H. rough ER and lysosomes J. smooth ER and nucleus Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 59. Multiple Choice, continued 2. Which features of plant cells are missing from this cell? F. cell wall and chloroplasts G. Golgi apparatus and mitochondria H. rough ER and lysosomes J. smooth ER and nucleus Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 60. Multiple Choice, continued 3. What is the function of the structure labeled A? A. making ATP B. making carbohydrates C. making proteins D. moving proteins through the cell Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 61. Multiple Choice, continued 3. What is the function of the structure labeled A? A. making ATP B. making carbohydrates C. making proteins D. moving proteins through the cell Standardized Test Prep Chapter 3
- 62. Section 3-3 multicellular organization In unicellular organisms , one cell can perform all the function of life . Most cells in multicellular organisms are specialized to perform one or a few function , because of cell specialization . The cells in multicellular organisms depend on the other cells in the organism for their survival.
- 63. Tissues , Organs , And organ systems • Cells are organized into tissues • Tissues: are groups of cells that carry out a specific function. • Types of tissues: 1- Epithelial tissue 2- Connective tissue 3- Muscle tissue 4- Nervous tissue
- 64. Types of tissue 1) Epithelial tissue : forms surface covering • Ex the outermost living layer of skin. 2) Connective tissue: supports and links other tissues. 3) Muscle tissue: is composed of cells that pulls against one another by contracting 4) Nervous tissue : is composed of cells that are specialized for transmitting and reciving messages
- 65. • Organ: is a group of tissues that are specialized to perform a specific function • Examples: Heart, kidney, liver, stomach, brain. stomach • Muscle tissue: causes movement • Connective tissue: supports and links stomach together • Epithelial tissue: secrete enzymes • Nervous tissue: transmits messages
- 66. Organ systems Organ system :- It is a group of organs that work together to perform a set or related tasks . Example: cardiovascular system, urinary system and respiratory systems. The different organ systems interact with each other to carry out processes of life Non of the body’s organ system could survive without the others.
- 67. plants also have tissues and organs Types of tissues in plants • Dermal tissue: forms outer surface of plant • Ground tissue: makes up a bulk of stems and roots • Vascular tissue: transports water through out the plant
- 68. Organs of plants • Roots • Stems • Leaves • Flowers
- 69. Colonial organisms • Some unicellular eukaryotes can lives in groups or colonies • A colonial organization: is a group of cells that are genetically identical and they live together example: green algae volvox. A hollow volvox sphere contains 500 to 60,000 cells Many cells in colony are specialized to perform a specific function example: outer cells use their flagella to move the colony through the water and a few of other cells are specialized to reproduce.
- 70. Volvox colony They are a border between unicellular and multicellular They are not unicellular because they live together They are not multicellular because they lack tissue and organ
Notas del editor
- n.S ( zhmaray lakanyate ka bo shash pallw 6 laya wata n= 6 )