Causes and Mechanisms of Cirrhosis
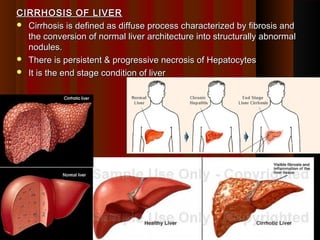
- 1. CIRRHOSIS OF LIVERCIRRHOSIS OF LIVER Cirrhosis is defined as diffuse process characterized by fibrosis andCirrhosis is defined as diffuse process characterized by fibrosis and the conversion of normal liver architecture into structurally abnormalthe conversion of normal liver architecture into structurally abnormal nodules.nodules. There is persistent & progressive necrosis of HepatocytesThere is persistent & progressive necrosis of Hepatocytes It is the end stage condition of liverIt is the end stage condition of liver 11
- 2. Characteristics are:Characteristics are: BridgingBridging FibrousFibrous septa in the form of delicate bands from Portal tosepta in the form of delicate bands from Portal to central, portal to portal & central to central or broad scarscentral, portal to portal & central to central or broad scars ParenchymalParenchymal NodulesNodules, are formed by regeneration of hepatocytes., are formed by regeneration of hepatocytes. Disruption of theDisruption of the architecturearchitecture of the entire liver.of the entire liver. The parenchymal cell injury and fibrosis are diffuse, extendingThe parenchymal cell injury and fibrosis are diffuse, extending throughout the liver.throughout the liver. Necrosis of hepatocytesNecrosis of hepatocytes IrreversibleIrreversible Progressive disorderProgressive disorder Entire Liver is involvedEntire Liver is involved 22
- 3. Cirrhosis can be classifiedCirrhosis can be classified histologicallyhistologically into three types.into three types. Micro nodular cirrhosisMicro nodular cirrhosis Is characterized by small nodules about 1 mm in diameter and isIs characterized by small nodules about 1 mm in diameter and is seen in alcoholic cirrhosis.seen in alcoholic cirrhosis. Macro nodular cirrhosisMacro nodular cirrhosis Is characterized by larger nodules of > 3mm in diameter .Is characterized by larger nodules of > 3mm in diameter . ( Viral Hepatitis)( Viral Hepatitis) Mixed typesMixed types (Alcoholic cirrhosis with time)(Alcoholic cirrhosis with time) 33
- 4. Aetiologicl ClassificationAetiologicl Classification Alcoholic Cirrhosis (60-70%)Alcoholic Cirrhosis (60-70%) Chronic viral hepatitis (10%)Chronic viral hepatitis (10%) Biliary Cirrhosis (5-10%)Biliary Cirrhosis (5-10%) Cryptogenic (unknown) (10-15%)Cryptogenic (unknown) (10-15%) Haemochromatosis (5%)Haemochromatosis (5%) αα1-antitrypsin deficiency1-antitrypsin deficiency Wilson's diseaseWilson's disease 44
- 5. Alcoholic Liver DiseaseAlcoholic Liver Disease ALD comprises of 3 distinct forms of Liver diseasesALD comprises of 3 distinct forms of Liver diseases Hepatic steatosis/ fatty LiverHepatic steatosis/ fatty Liver Alcoholic hepatitisAlcoholic hepatitis CirrhosisCirrhosis 55
- 6. HaemochromatosisHaemochromatosis Is defined as the excessive accumulation of body iron, most ofIs defined as the excessive accumulation of body iron, most of which deposited in the parenchymal cell of various organ particularlywhich deposited in the parenchymal cell of various organ particularly liver & pancreasliver & pancreas TypesTypes Hereditary/primary/idiopathicHereditary/primary/idiopathic Secondary – occuring as a secondary complications to a variety ofSecondary – occuring as a secondary complications to a variety of diseasesdiseases 66
- 7. Wilson’s DiseaseWilson’s Disease Is an autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism & isIs an autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism & is marked by accumulation of toxic levels of copper in many tissues inmarked by accumulation of toxic levels of copper in many tissues in many tissues & organs principally the liver, brain & eyemany tissues & organs principally the liver, brain & eye Primary biPrimary bi 77
- 8. Biliary cirrhosisBiliary cirrhosis Primary intrahepatic biliary cirrhosisPrimary intrahepatic biliary cirrhosis An autoimmune disease marked by the slow progressive destructionAn autoimmune disease marked by the slow progressive destruction of the small intrahepatic bile ducts.of the small intrahepatic bile ducts. Bile builds up in the liver and over time damages the tissue.Bile builds up in the liver and over time damages the tissue. This can lead to scarring, fibrosis and cirrhosisThis can lead to scarring, fibrosis and cirrhosis Secondary biliary cirrhosisSecondary biliary cirrhosis Results from obstruction to the major extra hepatic ductResults from obstruction to the major extra hepatic duct 88
- 9. Alpha1 antitrypsin deficiencyAlpha1 antitrypsin deficiency Is an autosomal recessicve disorder marked by abnormally low levels ofIs an autosomal recessicve disorder marked by abnormally low levels of ofof αα1-antitrypsin in serum1-antitrypsin in serum Predominantly synthesized in Hepatocytes & to less extent inPredominantly synthesized in Hepatocytes & to less extent in macrophagemacrophage 99
- 10. The major mechanisms that combine to create cirrhosis areThe major mechanisms that combine to create cirrhosis are Hepatocellular death,Hepatocellular death, Regeneration ,Regeneration , Progressive fibrosis and vascular changes.Progressive fibrosis and vascular changes. The development of cirrhosis requires that cell death occur over longThe development of cirrhosis requires that cell death occur over long periods of time and be accompanied by fibrosis.periods of time and be accompanied by fibrosis. Regeneration is a normal compensatory response to cell death.Regeneration is a normal compensatory response to cell death. Fibrosis is a wound-healing reaction that progresses to scarFibrosis is a wound-healing reaction that progresses to scar formation when the injury involves not only the parenchyma but alsoformation when the injury involves not only the parenchyma but also the supporting connective tissue.the supporting connective tissue. 1010
- 11. In the normal liver, interstitial collagens (types I and III) areIn the normal liver, interstitial collagens (types I and III) are concentrated in portal tracts and around central veins, withconcentrated in portal tracts and around central veins, with occasional bundles in the space of Disse.occasional bundles in the space of Disse. The collagen (reticulin) coursing alongside hepatocytes isThe collagen (reticulin) coursing alongside hepatocytes is composed of delicate strands of type IV collagen in the space ofcomposed of delicate strands of type IV collagen in the space of Disse.Disse. Ito cells (Lipocytes) & hepatocytes synthesize collagenIto cells (Lipocytes) & hepatocytes synthesize collagen 1111
- 12. PathogenesisPathogenesis The central pathogenetic process in cirrhosis is progressive fibrosis dueThe central pathogenetic process in cirrhosis is progressive fibrosis due to excess of collagen production & its depositionto excess of collagen production & its deposition In cirrhosis, types I and III collagen are deposited all over the lobule,In cirrhosis, types I and III collagen are deposited all over the lobule, creating delicate or broad septal tracts.creating delicate or broad septal tracts. Continued deposition of collagen in the space of Disse isContinued deposition of collagen in the space of Disse is accompanied by the loss of fenestrations in the sinusoidal endothelialaccompanied by the loss of fenestrations in the sinusoidal endothelial cells.cells. In the process -exchange of solutes between hepatocytes and plasmaIn the process -exchange of solutes between hepatocytes and plasma is disturbedis disturbed In particular, hepatocellular secretion of proteins (e.g., albumin,In particular, hepatocellular secretion of proteins (e.g., albumin, clotting factors) is greatly impaired.clotting factors) is greatly impaired. 1212
- 13. -Ito cells (perisinusoidal stellate cells) become activated during the-Ito cells (perisinusoidal stellate cells) become activated during the development of cirrhosis, and transform into myofibroblast-like cells.development of cirrhosis, and transform into myofibroblast-like cells. -And are stimulated to produce collagen & may be due to :-And are stimulated to produce collagen & may be due to : Chronic inflammation, with production of inflammatory cytokines suchChronic inflammation, with production of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, transforming growth factoras tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, transforming growth factor (TGF)- beta, and interleukin-1 by endogenous cells (Kupffer cells,(TGF)- beta, and interleukin-1 by endogenous cells (Kupffer cells, endothelial cells, hepatocytes, and bile duct epithelial cells)endothelial cells, hepatocytes, and bile duct epithelial cells) Direct stimulation by Toxins or their metabolitesDirect stimulation by Toxins or their metabolites Distortion of extracellular matrixDistortion of extracellular matrix 1313
- 14. 1414
- 15. Contraction of these "myofibroblasts“ (Ito Cells) constricts theContraction of these "myofibroblasts“ (Ito Cells) constricts the sinusoidal vascular channels.sinusoidal vascular channels. Remaining hepatocytes are stimulated to regenerate, and theyRemaining hepatocytes are stimulated to regenerate, and they proliferate as spherical nodules within the confines of the fibrousproliferate as spherical nodules within the confines of the fibrous septa.septa. 1515
- 16. The net outcome isThe net outcome is A fibrotic, nodular liver in which delivery of blood to hepatocytes isA fibrotic, nodular liver in which delivery of blood to hepatocytes is severely compromised, as is the ability of hepatocytes to secreteseverely compromised, as is the ability of hepatocytes to secrete substances into plasma.substances into plasma. Disruption of the interface between the parenchyma and portalDisruption of the interface between the parenchyma and portal tracts obliterates biliary channels as well.tracts obliterates biliary channels as well. Thus, the cirrhotic patient may develop jaundice and even hepaticThus, the cirrhotic patient may develop jaundice and even hepatic failure, despite having a liver of normal mass.failure, despite having a liver of normal mass. 1616
- 17. Pathogenesis(ALT)Pathogenesis(ALT) Injurious AgentInjurious Agent Liver cell necrosisLiver cell necrosis Chronic inflammationChronic inflammation Fibrosis Reactive hyperplasia of hepatocytes /Nodular re-growthFibrosis Reactive hyperplasia of hepatocytes /Nodular re-growth Vascular damage and derangementVascular damage and derangement Increased supply to other partsIncreased supply to other parts Diminished supply to some partsDiminished supply to some parts Disruption of lobular circulationDisruption of lobular circulation Obstruction of portal circulationObstruction of portal circulation Interference with hepatic functionInterference with hepatic function portal HTNportal HTN .. 1717
- 18. 1818 •Very low power microscopic view of the liver. •The parenchyma shows darker tan nodules of varying sizes. •These nodules are composed of hepatocytes. •The paler areas in between are collagen.
- 19. Nodular , firm liver. The nodules seen here are larger than 3 mm and,Nodular , firm liver. The nodules seen here are larger than 3 mm and, hence, this is an example of "macronodular" cirrhosis.hence, this is an example of "macronodular" cirrhosis. 1919
- 20. micronodular cirrhosis. The regenerative nodules are quite small, averagingmicronodular cirrhosis. The regenerative nodules are quite small, averaging less than 3 mm in size. The most common cause for this is chronic alcoholism.less than 3 mm in size. The most common cause for this is chronic alcoholism. 2020
- 21. Here is another example of micronodular cirrhosis. Note that theHere is another example of micronodular cirrhosis. Note that the liver also has a yellowish hue, indicating that fatty change (alsoliver also has a yellowish hue, indicating that fatty change (also caused by alcoholism) is present. 2121
- 22. A close-up view of a micronodular cirrhosis in a liver with fatty changeA close-up view of a micronodular cirrhosis in a liver with fatty change demonstrates the small, yellow nodules.demonstrates the small, yellow nodules. 2222
- 23. macronodular cirrhosis. Viral hepatitis (B or C) is the most common cause formacronodular cirrhosis. Viral hepatitis (B or C) is the most common cause for macronodular cirrhosis. Wilson's disease and alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency alsomacronodular cirrhosis. Wilson's disease and alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency also can produce a macronodular cirrhosis.can produce a macronodular cirrhosis. 2323
- 24. Microscopically with cirrhosis, the regenerative nodules of hepatocytesMicroscopically with cirrhosis, the regenerative nodules of hepatocytes are surrounded by fibrous connective tissue that bridges between portalare surrounded by fibrous connective tissue that bridges between portal tracts. Within this collagenous tissue are scattered lymphocytestracts. Within this collagenous tissue are scattered lymphocytes 2424
- 25. CLINICAL FEATURES OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSISCLINICAL FEATURES OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS Hepatomegaly (although liver may also be small)Hepatomegaly (although liver may also be small) JaundiceJaundice AscitesAscites Circulatory changes - Spider telangiectasia, palmar erythema, cyanosisCirculatory changes - Spider telangiectasia, palmar erythema, cyanosis Endocrine changes - Loss of libido, hair loss,Endocrine changes - Loss of libido, hair loss, Men: gynaecomastia, testicular atrophy, impotenceMen: gynaecomastia, testicular atrophy, impotence Women: breast atrophy, irregular menses, amenorrhoeaWomen: breast atrophy, irregular menses, amenorrhoea Haemorrhagic tendency- Bruises, purpura, epistaxis, menorrhagiaHaemorrhagic tendency- Bruises, purpura, epistaxis, menorrhagia Portal hypertension - Splenomegaly, collateral vessels, varicealPortal hypertension - Splenomegaly, collateral vessels, variceal bleeding, fetor hepaticusbleeding, fetor hepaticus Hepatic (portosystemic) encephalopathyHepatic (portosystemic) encephalopathy Other features - Pigmentation, digital clubbingOther features - Pigmentation, digital clubbing 2525
- 26. Complications of Hepatic CirrhosisComplications of Hepatic Cirrhosis Portal hypertensionPortal hypertension AscitisAscitis Renal failureRenal failure Hepatic encephalopathyHepatic encephalopathy InfectionsInfections Hepatocellular carcinomaHepatocellular carcinoma 2626
- 27. PORTAL HYPERTENSION / PHTPORTAL HYPERTENSION / PHT PHT is characterized by prolonged elevation of the portal venousPHT is characterized by prolonged elevation of the portal venous pressure (normally 2-5 mmHg).pressure (normally 2-5 mmHg). Pts developing C/F or Complications of PTH usually have portalPts developing C/F or Complications of PTH usually have portal venous pressures (PVP) above 12 mmHg.venous pressures (PVP) above 12 mmHg. PathogenesisPathogenesis PVP is determined by the portal flow and portal vascular resistance.PVP is determined by the portal flow and portal vascular resistance. Increased vascular resistance is usually the main factor producingIncreased vascular resistance is usually the main factor producing portal hypertension, irrespective of its causeportal hypertension, irrespective of its cause 2727
- 28. CAUSES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSIONCAUSES OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION IntrahepaticIntrahepatic Cirrhosis – most commonCirrhosis – most common Massive fatty changes, miliary TB, SchistosomiasisMassive fatty changes, miliary TB, Schistosomiasis PosthepaticPosthepatic Right sided heart failure (Common)Right sided heart failure (Common) Obstructon of hepatic vein - Budd-Chiari syndrome (Hepatic veinObstructon of hepatic vein - Budd-Chiari syndrome (Hepatic vein thrombosis)thrombosis) PrehepaticPrehepatic Portal vein thrombosisPortal vein thrombosis Massive splenomegalyMassive splenomegaly 2828
- 29. 2929
- 30. PathophysiologyPathophysiology PHT leads to reduction in the flow of blood to the liver andPHT leads to reduction in the flow of blood to the liver and simultaneously to the collateral vessels,simultaneously to the collateral vessels, Allowing portal blood to bypass the liver and enter the systemicAllowing portal blood to bypass the liver and enter the systemic circulation directly.circulation directly. Collateral vessel formation is widespread but occurs especially theCollateral vessel formation is widespread but occurs especially the oesophagus, stomach, rectum and in the anterior abdominal walloesophagus, stomach, rectum and in the anterior abdominal wall Half or more (and occasionally almost all) of the portal blood flowHalf or more (and occasionally almost all) of the portal blood flow can be shunted directly to the systemic circulation.can be shunted directly to the systemic circulation. 3030
- 31. Clinical featuresClinical features Result principally from portal venous congestion and collateral vesselResult principally from portal venous congestion and collateral vessel formation.formation. Splenomegaly is a cardinalSplenomegaly is a cardinal Collateral vessels may be visible on the anterior abdominal wall andCollateral vessels may be visible on the anterior abdominal wall and occasionally several radiate from the umbilicus to form a caputoccasionally several radiate from the umbilicus to form a caput medusae.medusae. The most important collateral vessels occur in the oesophagus andThe most important collateral vessels occur in the oesophagus and stomach, where they can cause severe bleeding.stomach, where they can cause severe bleeding. Rectal varices also cause bleedingRectal varices also cause bleeding Fetor hepaticus results from portosystemic shunting of blood, whichFetor hepaticus results from portosystemic shunting of blood, which allows mercaptans to pass directly to the lungsallows mercaptans to pass directly to the lungs 3131
- 32. Clinical effects OF PORTAL HYPERTENSIONClinical effects OF PORTAL HYPERTENSION 4 major clinical effects are4 major clinical effects are AscitesAscites Portosystemic venous shuntPortosystemic venous shunt Caput medussa, Oesophagastric Varices bleeding, rectalCaput medussa, Oesophagastric Varices bleeding, rectal hemorroids etchemorroids etc Congestive splenomegalyCongestive splenomegaly Hepatic encephalopathyHepatic encephalopathy 3232
- 33. 3333
- 34. 3434 AscitisAscitis Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavityAbnormal accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity CausesCauses Common causesCommon causes Cirrhosis of liverCirrhosis of liver Cardiac failureCardiac failure Malignant disease – hepatic, peritonealMalignant disease – hepatic, peritoneal OthersOthers Hypoproteinaemia - Nephrotic syndrome, Protein losing enteropathy,Hypoproteinaemia - Nephrotic syndrome, Protein losing enteropathy, MalnutritionMalnutrition Hepatic venous occlusionHepatic venous occlusion Infection – T.B., BacterialInfection – T.B., Bacterial Lymphatic obstructionLymphatic obstruction
- 35. In Cirrhosis of liver, Ascites is due to In Cirrhosis of liver, Ascites is due to 3535
- 36. Hepatic Failure / Hepatocellular FailureHepatic Failure / Hepatocellular Failure Is a state that occurs due to loss of 80 to 90% hepatic functionsIs a state that occurs due to loss of 80 to 90% hepatic functions Failure can beFailure can be Acute – with rapid onset e.g. in cases of massive necrosis due toAcute – with rapid onset e.g. in cases of massive necrosis due to poisoning, less commonly acute hepatitispoisoning, less commonly acute hepatitis Chronic & sometimes recurring of slow onset e.g. in cirrhosis orChronic & sometimes recurring of slow onset e.g. in cirrhosis or chronic hepatitischronic hepatitis 3636
- 37. HEPATIC (PORTOSYSTEMIC) ENCEPHALOPATHYHEPATIC (PORTOSYSTEMIC) ENCEPHALOPATHY Hepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused byHepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric syndrome caused by liver disease.liver disease. As encephalopathy progresses, confusion is followed by coma.As encephalopathy progresses, confusion is followed by coma. 3737
- 38. Aetiopathosenesis (acute & chronic )Aetiopathosenesis (acute & chronic ) The basic cause is same in both forms but the mechanism isThe basic cause is same in both forms but the mechanism is somewhat differentsomewhat different Diminished detoxification of toxic intestinal nitrogenous compoundsDiminished detoxification of toxic intestinal nitrogenous compounds 3838 Increased in blood NH3 etc Toxic effect on brain Appearance of abnormal amines in systemic circulation Interference with neurotransmission
- 39. CLINICAL GRADING OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHYCLINICAL GRADING OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Clinical grade Clinical signsClinical grade Clinical signs Grade 1 Poor concentration, slurred speech, slowGrade 1 Poor concentration, slurred speech, slow mentation,mentation, disordered sleep rhythmdisordered sleep rhythm Grade 2 Drowsy but easily rousable, occasional aggressiveGrade 2 Drowsy but easily rousable, occasional aggressive behaviour, lethargicbehaviour, lethargic Grade 3 Marked confusion, drowsy, sleepy but responds toGrade 3 Marked confusion, drowsy, sleepy but responds to pain andpain and voice, gross disorientationvoice, gross disorientation Grade 4 Unresponsive to voice, may or may not respond toGrade 4 Unresponsive to voice, may or may not respond to painfulpainful stimuli, unconsciousstimuli, unconscious 3939
- 40. Hepatorenal syndromeHepatorenal syndrome Refers to the appearance of renal failure in a person with severeRefers to the appearance of renal failure in a person with severe liver disease without primary abnormalities of the kidneysliver disease without primary abnormalities of the kidneys themselves.themselves. Kidney function promptly improves if hepatic failure is reversed.Kidney function promptly improves if hepatic failure is reversed. Although the exact cause is unknown, evidence points to splanchnicAlthough the exact cause is unknown, evidence points to splanchnic and systemic vasodilation, leading to severe reduction of renaland systemic vasodilation, leading to severe reduction of renal blood flow.blood flow. Onset of this syndrome is typically heralded by a drop in urineOnset of this syndrome is typically heralded by a drop in urine output, associated with rising blood urea nitrogen and creatinineoutput, associated with rising blood urea nitrogen and creatinine values.values. 4040
