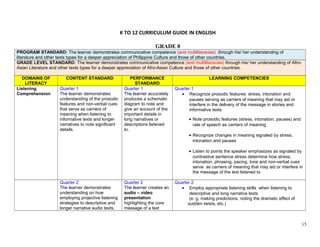
K TO 12 CURRICULUM GUIDE IN ENGLISH 8
- 1. K TO 12 CURRICULUM GUIDE IN ENGLISH GRADE 8 PROGRAM STANDARD: The learner demonstrates communicative competence (and multiliteracies) through his/ her understanding of literature and other texts types for a deeper appreciation of Philippine Culture and those of other countries. GRADE LEVEL STANDARD: The learner demonstrates communicative competence (and multiliteracies) through his/ her understanding of Afro- Asian Literature and other texts types for a deeper appreciation of Afro-Asian Culture and those of other countries. DOMAINS OF LITERACY CONTENT STANDARD PERFORMANCE STANDARD LEARNING COMPETENCIES Listening Comprehension Quarter 1 The learner demonstrates understanding of the prosodic features and non-verbal cues that serve as carriers of meaning when listening to informative texts and longer narratives to note significant details. Quarter 1 The learner accurately produces a schematic diagram to note and give an account of the important details in long narratives or descriptions listened to. Quarter 1 • Recognize prosodic features: stress, intonation and pauses serving as carriers of meaning that may aid or interfere in the delivery of the message in stories and informative texts • Note prosodic features (stress, intonation, pauses) and rate of speech as carriers of meaning • Recognize changes in meaning signaled by stress, intonation and pauses • Listen to points the speaker emphasizes as signaled by contrastive sentence stress determine how stress, intonation, phrasing, pacing, tone and non-verbal cues serve as carriers of meaning that may aid or interfere in the message of the text listened to Quarter 2 The learner demonstrates understanding on how employing projective listening strategies to descriptive and longer narrative audio texts, Quarter 2 The learner creates an audio – video presentation highlighting the core message of a text Quarter 2 • Employ appropriate listening skills when listening to descriptive and long narrative texts (e. g. making predictions, noting the dramatic effect of sudden twists, etc.) 15
- 2. helps him/her to validate information, opinion, or assumption to participate well in specific communicative context . The learner demonstrates understanding of adjusting listening strategies (marginal, selective, attentive, critical) in relation to the main purpose of listening, one’s familiarity with the topic and difficulty of the text describing a process and narrating longer stories to suit the listening text and task. • listened to. • Employ projective listening strategies with longer stories • Listen to determine conflicting information aired over the radio and television • Listen for clues to determine pictorial representations of what is talked about in a listening text Quarter 3 The learner demonstrates understanding in validating information, opinions, or assumptions made by a speaker to arrive at sound decisions on critical issues. Quarter 3 The learner proficiently writes an editorial article concerning an issue raised by the speaker in a text listened to. Quarter 3 • Determine the persons being addressed in an informative talk, the objective/s of the speaker and his/her attitude on the issues Use attentive listening strategies with informative texts • Note clues and links to show the speaker’s stand and assumptions • Listen for clues and links to show the speaker’s train of thoughts Determine the stand of the speaker on a given issue Listen to get the different sides of social, moral, 16
- 3. and economic issues affecting a community Quarter 4 The learner demonstrates understanding of how the orchestration of harmony, unison, rhythm and the structure of narratives and other text types enable him or her to appreciate their richness. Quarter 4 The learner creatively renders a choric interpretation of a text listened to • Quarter 4 • Process speech delivered at different rates by making inferences from what was listened to • Use syntactic and lexical clues to supply items not listened to • Anticipate what is to follow in a text listened to considering the function/s of the statements made • Express appreciation for texts orally interpreted noting harmony, unison, and rhythm. Listen to appreciate the tune and the narrative structure of ballads • Listen to appreciate harmony, unison, and rhythm in choric interpretations. Oral Language and Fluency Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how to speak in clear, correct English appropriate for a certain situation, purpose and audience. Quarter 1 • The learner actively participates in a conversational dialogue about school/environmenta l issues or any current social concerns. Quarter 1 • Use appropriate registers to suit the intended audience, and variation in intonation and stress for emphasis and contrast o Express feelings and attitudes by utilizing contrastive stress and variations of tone and tempo o Use stress, intonation, and juncture to signal changes in meaning Quarter 2 Quarter 2 Quarter 2 17
- 4. • The learner demonstrates understanding of the various means on how figurative and academic language can be used in various communication settings. • The learner joins actively in a panel discussion on a current issue or concern. • Ask for and give information, and express needs, opinions, feelings, and attitudes explicitly and implicitly in an informative talk • Formulate responses to questions noting the types of questions raised (yes-no, wh-questions, alternative, modals, embedded) • Make inquiries • Give information obtained from mass media: newspapers, radio, television • Highlight important points in an informative talk using multi-media resources Quarter 3 The learner demonstrates understanding of using turn- taking strategies in extended conversations to effectively convey information. Quarter 3 The learner proficiently conducts a formal, structured interview of a specific subject. • Quarter 3 • Use appropriate turn-taking strategies (topic nomination, topic development, topic shift, turn-getting, etc.) in extended conversations Interview persons to get opinions about certain issues Respond orally to ideas and needs expressed in face-to-face interviews in accordance with the intended meaning of the speaker Use communication strategies (e.g. paraphrase, translations, and circumlocution) to repair breakdown in communication • Quarter 4 The learner demonstrates Quarter 4 The learner Quarter 4 • Arrive at a consensus on community issues by assessing 18
- 5. understanding of speech functions and forms as indicators of meaning. competently delivers an informative speech using multi- media resources to highlight important points. statements made React to information obtained from talks • Interview persons to get their opinions about social issues affecting the community Agree/Disagree with statements, observations and responses made when issues affecting the community Infer the function/s of utterances and respond accordingly taking into account the context of the situation and the tone used • Vocabulary Enhancement (Subsumed in all domains) Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the strategies for coping with the unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse to arrive at meaning. Quarter 1 The learner creatively produces an e-portfolio of vocabulary illustrating the use of varied strategies. Quarter 1 • Develop strategies for coping with unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse o Differentiate between shades of meaning by arranging words in a cline o Guess the meaning of idiomatic expressions by noting keywords in expressions, context clues, collocations, clusters, etc. o Arrive at the meaning of structurally complex and ambiguous sentences by deleting expansions to come up with kernel sentences Quarter 2 • The learner Quarter 2 The learner creatively Quarter 2 • Develop strategies for coping with unknown 19
- 6. demonstrates understanding of the strategies for coping with the unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse to arrive at meaning. prepares a comparative log of academic and figurative language reflected in documents with the same themes. words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse o Identify the derivation of words o Define words from context and through word analysis (prefix, roots, suffixes) o Use collocations of difficult words as aids in unlocking vocabulary o Arrive at the meaning of structurally complex and ambiguous sentences by separating kernel sentences from modification structures and expansions Quarter 3 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the strategies for coping with the unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse to arrive at meaning. Quarter 3 The learner creatively produces a frequency word list. Quarter 3 • Develop strategies for coping with unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse o Identify the derivation of words o Define words from context and through word analysis (prefix, roots, suffixes o Use collocations of difficult words as aids in unlocking vocabulary • Arrive at the meaning of structurally complex and ambiguous sentences by separating kernel sentences from modification structures and expansions. Quarter 4 • The learner demonstrates Quarter 4 The learner proficiently produces a glossary Quarter 4 • Develop strategies for coping with unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse 20
- 7. understanding of the strategies for coping with the unknown words and ambiguous sentence structures and discourse to arrive at meaning. of words related to specific disciplines. o Identify the derivation of words o Define words from context and through word analysis (prefix, roots, suffixes) o Use collocations of difficult words as aids in unlocking vocabulary • Arrive at the meaning of structurally complex and ambiguous sentences by separating kernel sentences from modification structures and expansions Reading and Comprehension Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the different reading styles to suit the text and one’s purpose for reading. Quarter 1 The learner produces a Reading Log showing various entries like the choice of reading materials, the type of reading employed, etc. Quarter 1 • Adjust reading speed based on one’s purpose for reading and the type of materials read • Use different reading styles to suit the text and one’s purpose for reading • Scan rapidly for sequence signals or connectors as basis for determining the rhetorical organization of texts • Skim to determine the author’s key ideas and purpose by answering questions raised after surveying the text • Read closely to select appropriate details from a selection for specific purposes Quarter 2 • The learner demonstrates understanding of textual Quarter 2 The learner proficiently uses advanced organizers/ illustrations showing Quarter 2 • Evaluate content, elements, features, and properties of a reading or viewing selection using a set of criteria developed in consultation (with peers and the teacher) 21
- 8. relationships using non- linear forms and graphics to obtain information from linear and non-linear texts. textual relationships. • Explain visual-verbal relationships illustrated in tables, graphs, information maps commonly used in content area texts Transcode information from linear to non-linear texts and vice-versa Explain illustrations from linear to non-linear texts and vice versa Organize information illustrated in tables, graphs and maps Quarter 3 • The learner demonstrates understanding of varied reading approaches to make sense and develop appreciation for the different text types. Quarter 3 The learner creatively produces a digital chart of various text types with clickable features. Quarter 3 • Utilize varied reading strategies to process information in a text • Recognize the propaganda strategies used in advertisements and consider these in formulating hypotheses • Distinguish between facts from opinions • Use expressions that signal opinions (e.g. seems, as I see it) • Note the function of statements made as the text unfolds and use it as a basis for predicting what is to follow • Express emotional reactions to what was asserted or expressed in a text • Employ approaches best suited to a text Note the functions of statements as they unfold 22
- 9. and consider the data that might confirm/disconfirm hypothesis Examine for bias Determine the validity and adequacy of proof statements to support assertions React critically to the devices employed by a writer to achieve his/her purpose Quarter 4 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how to abstract information presented in different text types and to note explicit and implicit signals used by the writer. Quarter 4 The learner prepares an abstract of a text read. Quarter 4 • Utilize knowledge of the differences among text types (instructional, explanatory, recount, persuasive, informational and literary) as an aid in processing information in the selection read or viewed • Assess the content and function of each statement in a text with a view of determining the information structure of the text • Abstract information from the different text types by noting explicit and implicit signals used by the writer • Interpret instructions, directions, notices, rules and regulations • Locate and synthesize essential information found in any text Distinguish the statement of facts from beliefs. Evaluate the accuracy of the information. 23
- 10. Draw conclusions from the set of details. Point out relationships between statements. Distinguish between general and specific statements. • Literature Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the different genres through the types contributed by Afro- Asian countries to express appreciation for Afro-Asian heritage. Quarter 1 The learner creatively and proficiently performs in a choral reading of a chosen Afro-Asian poem. • Discover literature as a means of understanding the human being and the forces he/she to contend with • Discover through literature the symbiotic relationship between man and his environment and the need of the former to protect the latter • Demonstrate a heightened sensitivity to the needs of others for a better understanding of man • Discover through literature the links between one’s life and the lives of people throughout the world • Highlight the need for a more just and equitable distribution of resources Quarter 2 •The learner demonstrates understanding of how significant human experiences are best captured in various literary forms that inspire humans to bring out the best in them. Quarter 2 The learner creatively compiles Afro-Asian literary pieces as accounts of experiential learning. Quarter 2 • Show understanding and appreciation for the different genres with emphasis on types contributed by Asian countries (i.e. Haiku, Tanka, etc.) • • Point out the elements of plays and playlets • Determine the macro discourse patterns of essays and the macro discourse signals used to establish meaning relationships in the essay • Determine the author’s tone and purpose for writing the 24
- 11. essay • Point out how the choice of title, space allotment, imagery, choice of words, figurative language, etc. contribute to the theme Explain figurative language used Express appreciation for sensory images in literary forms Show understanding of the text by paraphrasing passages Quarter 3 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the different genres to heighten literary competence. Quarter 3 The learner produces a critical review of articles with the same themes but different genres. Quarter 3 • Discover Philippine and Afro Asian literature as a means of expanding experiences and outlook and enhancing worthwhile universal human values • Express appreciation for worthwhile Asian traditions and the values they represent • Assess the Asian identity as presented in Asian literature and oneself in the light of what makes one an Asian • Identify oneself with other people through literature taking note of cultural differences so as to get to the heart of problems arising from them Quarter 4 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how literature mirrors the realities of life and depicts Quarter 4 The learner produces an e-literary folio which captures significant human experiences. Quarter 4 • Point out the role of literature in enabling one to grow in personhood • Discriminate between what is worthwhile and what is not through literature 25
- 12. human aspirations. • Distinguish as positive values humility, resourcefulness, self-reliance and the ability to look into oneself, and accept one’s strengths and weaknessess Viewing Comprehension Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the different text types and genres of programs viewed to effectively derive information and find meaning in them Quarter 1 The learner produces program portfolio that monitors his/her progress as a viewer (in terms of interest, preference, and reflections on individual viewing behaviors). • Organize information extracted from a program viewed • Compare and contrast basic genres of programs viewed • Narrate events logically • Validate mental images of the information conveyed by a program viewed • Respond to questions raised in a program viewed Quarter 2 •The learner demonstrates understanding of the different text types and genres of programs viewed to effectively derive information and find meaning in them. Quarter 2 The learner effectively writes reactions to movies viewed. (movie review) The learner presents a review of a program viewed. Quarter 2 • Discern positive and negative messages conveyed by a program viewed • React appropriately and provide suggestions based on an established fact • Decode the meaning of unfamiliar words using structural analysis • Follow task- based directions shown after viewing • Interpret the big ideas/key concepts implied by the facial expressions of interlocutors Quarter 3 • The learner Quarter 3 The learner produces a reaction paper to a Quarter 3 • Analyze the elements that make up reality and fantasy 26
- 13. demonstrates understanding of the various analytical and evaluative techniques employed in critical viewing. program viewed. from a program viewed • Compare and contrast one’s own television-viewing behavior with other viewers’ viewing behavior • Organize an independent and systematic approach in critiquing various reading or viewing selection Quarter 4 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how viewing conventions affect the way viewers grasp, interpret, and evaluate the meaning of a program viewed. Quarter 4 The learner puts up a model television production incorporating viewing conventions. Quarter 4 • Recognize the principles of lay outing in viewing a material • Explore how colors appeal to viewer’s emotions • Identify basic camera angles • Ascertain how balance created by symmetry affects visual response to a program viewed • Differentiate between vantage points and viewing Writing Quarter 1 • The learner demonstrates understanding of giving valuable personal information and information on social events and issues by accomplishing different forms to effectively function in school and in community. . Quarter 1 The learner proficiently prepares a brochure on the dangers of smoking/drugs and other social issues and concerns. The learner writes a personal narratives. The learner creates a Quarter 1 • Accomplish forms and prepare notices • Write the information asked for in the following forms: School forms Bank forms Order slips Evaluation forms Survey forms Bills, telecom, etc. • Write notices (e.g. posters, slogans, advertisements 27
- 14. blog on the internet commenting on social/economic issues and concerns. that relate to social events Quarter 2 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the power of language structures and forms in shaping people’s reactions, perceptions, points of view, and beliefs in local, national and global communities. Quarter 2 The learner conducts an opinion poll, interprets, and presents the findings having a local-based or national issue as reference. Quarter 2 • Use non-linear texts and outlines to show relationships between ideas Transcode ideas from texts to concept maps Make a write-up of ideas presented in concept maps Use three-step words, phrasal and sentence outlines to organize ideas • Transcode information from linear to non-linear texts and vice versa Employ concept mapping (circle, bubble, linear, etc.) as aids in taking down notes and organizing ideas Use outlines to sum up ideas taken from texts Use non-linear text outlines and notes as aids in the preparation of a research paper Quarter 3 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how to have a good command and facility of the English Language necessary to produce writing in different genres Quarter 3 The learner produces an e-journal of poetry & prose entries with emphasis on content and writing style. Quarter 3 • Use specific cohesive and literary devices to construct integrative literary and expository reviews, critiques, research reports, and scripts for broadcast communication texts, including screenplays • Produce different text types and sub-types 28
- 15. and modes. Expand ideas in well-constructed paragraphs observing cohesion, coherence and appropriate modes of paragraph development • Give and respond to feedback on one’s paper in the revision process Use grammatical structure and vocabulary needed to effectively emphasize particular points • Use appropriate modes of paragraph development to express one’s ideas, needs, feelings and attitudes • Use a variety of cohesive devices to make the flow of thoughts from one sentence to another smoothly and effortlessly • Write short personal narratives to support an assertion • Organize information gathered from primary and secondary sources using a graphic organizer and a simple topic outline • Do self and peer editing using a set of criteria • Revise a piece of short personal writing in terms of content, style, and mechanics collaboratively and independently. Quarter 4 •The learner demonstrates understanding Quarter 4 The learner makes a write-up of an Quarter 4 • Organize one’s thoughts and adopt the appropriate writing style in letters, resumes, critiques, etc. using 29
- 16. of how to have a good command and facility of the English Language necessary to produce writing in different genres and modes. interview. appropriate styles (formal and formal)and audience in mind • Employ interactional functions of language in different genres and modes of writing (pen-pal letters, letters of invitation, a “yes” and “no” letters, book reviews, interview write-ups, journal entries, etc.) • Write reflections on learning experiences in diary and journal entries • Write summaries of books read • Employ varied strategies (condensing, deleting, combining, embedding) when summarizing materials read • Write reactions to books read • Show respect for intellectual property rights by acknowledging citations made • Acknowledge citations by indicating in a bibliography sources used • Use writing conventions to indicate acknowledgement of resources • Use quotation marks or hanging indentations for direct quotes • Use in-text citation • Arrange bibliographic entries of text cited from books 30
- 17. and periodicals • Grammar Quarter 1 The learner demonstrates understanding of well- constructed paragraphs using appropriate modes of development and language structures to express one’s ideas, needs, feelings and attitudes The learner demonstrates understanding of how language is instrumental in communicating thoughts, and feelings. Quarter 1 The learner effectively writes a personal narrative or informative text. The learner proficiently writes a description of a process. Quarter 1 Uses: o varied adjective complementation o appropriate idioms, collocations, and fixed expression o coordinators o subordinators o other appropriate devices for emphasis Formulates: o correct complex and compound-complex sentences o correct conditional statements o appropriate parenthetical expressions o meaningful expanded sentence (following balance, parallelism, and modification) • Quarter 2 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how grammatically correct sentences ensure an effective discourse. • The learner demonstrates understanding of how the knowledge of grammar enables one to successfully deliver information. Quarter 2 The learner composes a meaningful and grammatically correct composition. The learner writes a progress/ interim report of a program or advocacy Quarter 2 Uses: o varied adjective complementation o appropriate idioms, collocations, and fixed expression o coordinators o subordinators other appropriate devices for emphasis • formulates: o correct complex and compound-complex sentences o correct conditional statements o appropriate parenthetical expression meaningful expanded sentence (following balance, parallelism, 31
- 18. and modification) Quarter 3 • The learner demonstrates understanding of how the use of Standard English conventions facilitates interaction and transaction. Quarter 3 The learner creatively produces a tourist guide brochure Quarter 3 Uses: o varied adjective complementation o appropriate idioms, collocations, and fixed expression o coordinators o subordinators other appropriate devices for emphasis • formulates: o correct complex and compound-complex sentences o correct conditional statements o appropriate parenthetical expressions meaningful expanded sentence (following balance, parallelism, and modification) Quarter 4 • The learner demonstrates understanding of the set of structural rules that govern various communication situations. Quarter 4 The learner innovatively presents an Ad promoting a government bill or a city ordinance. Quarter 4 Uses: o varied adjective complementation o appropriate idioms, collocations, and fixed expression o coordinators o subordinators other appropriate devices for emphasis • formulates: o correct complex and compound-complex sentences o correct conditional statements o appropriate parenthetical expressions meaningful expanded sentence (following balance, parallelism, and modification) 32
- 19. Attitude towards language, literacy and literature (Subsumed in all domains) Quarter 1 • Ask sensible questions on his/her initiative Quarter 2 • Express a different opinion without being difficult Quarter 3 • Give credence to well-though out ideas Quarter 4 • Set new goals for learning on the basis of self- assessment made Study Strategies (Subsumed in Reading, Literature, and Writing) Quarter 1 The learner demonstrates understanding of how to gather data using library and electronic resources to locate information that bring about diversity and/or harmony among Afro – Asians through the study of their traditions and beliefs. Quarter 1 The learner creatively writes an interesting Cultural Report. Quarter 1 Gather data using library and electronic resources consisting of general references: atlas, periodical index, periodicals and internet sources/ other websites to locate information • Use periodical index to locate information in periodicals • Gather data using the general references: encyclopedia, dictionary • Get and assess current information from newspaper and other print and non-print media Quarter 2 The learner demonstrates understanding of how proper citations of references and materials used establish the credibility of a Quarter 2 The learner produces research appendices following the correct citation entries and format Quarter 2 Acknowledge citations by preparing the bibliography of the various sources used • Observe correct format in bibliographical entries • Use writing conventions to indicate acknowledgement of sources 33
- 20. report or a research paper. Quarter 3 The learner demonstrates understanding of how information gathering skills and data collection strategies ensure quality research Quarter 3 The learner produces a clip report on the various sources of data collected Quarter 3 Derive information from various text types and sources using the card catalog, vertical file, index, microfiche (microfilm) CD ROM, internet etc. • Use locational skills to gather and synthesize information from general and first-hand sources of information • Get vital information from various websites • Extract accurately the required information from sources read and viewed to reject irrelevant details Quarter 4 The learner demonstrates understanding of how the employment of study strategies coupled with research skills lead to a well- written paper Quarter 4 The learner produces a research paper based on school/ community problem. Quarter 4 • Use multi step word and phrasal outlines to organize ideas • Engage in systematic conduct of a research by going through series of processes • Organize logically information gathered • Apply the correct treatment of data and the soundness of research conclusion. 34
- 21. 35
