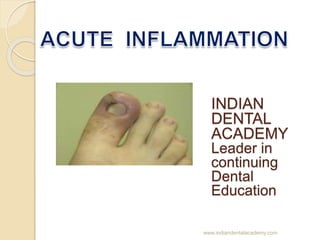
acute inflammation
- 2. REFERENCES • Robbins,Kumar,Abbas,Mitchell,Fausto. Textbook of Basic Pathology ,8th Edition. • Harshmohan.Textbook of Essential pathology, 5th Edition. •Walter and Isreal. General pathology 6th edition. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 3. Learning objectives: At the end of the seminar learner should be able to: 1. Define inflammation. 2. Enumerate cardinal signs, causes of inflammation. 3. Describe events in acute inflammation . 4. Describe inflammatory mediators. 5. Describe outcomes, morphological patterns of inflammation. 6. Describe the clinical importance of inflammation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 4. History: Signs of inflammation were described in an Egyptian papyrus, (3000 B.C.) Celsus, a roman writer, in 1st century A.D., first listed four signs of inflammation Rubor - Redness Tumor - Swelling Calor - Heat Dolor - Pain Rudolf virchow (1858), added fifth sign, Loss of function (functio laesa) www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 6. Definitions : “The local response of living mammalian tissue to injury due to any agent”. “Inflammation is a protective response intended to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury as well as the necrotic cells and tissues resulting from the original insult.” www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 7. CAUSES 1. Physical agents 2. Chemical agents 3. Infective agents 4. Immunological agents heat, cold, radiation and mechanical trauma. organic and inorganic poisons. bacteria, viruses and their toxins. cell-mediated and antigen- antibody reactions. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 8. Inflammation Acute Chronic Acute versus chronic inflammation are distinguished by the duration and the type of infiltrating inflammatory cells www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 9. “It is a rapid response to injury or microbes and other foreign substances that is designed to deliver leucocytes and plasma proteins to sites of injury.” www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 10. • The changes in acute inflammation can be described under the following headings- 1 ) Vascular changes - Changes in vascular caliber and flow. - Increased vascular permeability. 2) Cellular events - Exudation of leucocytes - Phagocytosis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 12. Vascular events Alteration in the microvasculature is the earliest response to tissue injury, they are: Hemodynamic changes Increased vascular permeability www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 13. Haemodynamic changes The earliest feature of inflammatory response results from change in vascular flow and caliber of small blood vessel in injured tissue. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 14. 1) Transient vasoconstriction of arterioles: -Immediate vascular response irrespective of the type of injury. -Vasoconstriction in mild to moderate injury: 3-5 seconds -In severe injury : lasts upto 5 minutes www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 15. 2) Persistent progressive vasodilatation : -Mainly involves arterioles, venules . - Changes are seen within half an hour. - Vasodilatation results in increased blood volume in the area responsible for heat and redness. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 17. 3) Elevation of local hydrostatic pressure : Results in transudation of fluid into extracellular space causing swelling at the site of inflammation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 18. 4)Slowing or stasis of the microcirculation Caused by prolonged vasodilatation and increased permeability of microvasculature Increased concentration of red cells Increased blood viscosity www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 19. 5) leukocyte margination ( peripheral orientation) Leukocytes mainly neutrophils stick to the vascular endothelium moves and migrates through endothelial gaps into extracellular space called as emigration. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 21. Triple response: It demonstrates features of haemodynamic changes in inflammation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 22. The Triple Response Red line, Flare& Wheal (Lewis, 1927) Take a blunt instrument and draw a line on your forearm. • Red line appears due to vasodilatation of capillaries and venules in response to injury. • Flare is red irregular zone or flush surrounding the red line, that develops due to arteriolar dilation. • Wheal a zone of edema due to fluid exudation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 24. Vascular changes & fluid leakage during acute inflammation lead to Edema in a process called Exudation Transudate •Result of hydrostatic imbalance •Low protein content •Specific gravity < 1.015 Exudate •Result of inflammation Vascular permeability •High protein content •specific gravity >1.020 www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 25. STARLING’S HYPOTHESIS Fluid balance is maintained by 2 opposing sets of forces: 1) Intravascular hydrostatic pressure & interstitial osmotic pressure – Causes outward movement of fluid from circulation. 2) Intravascular osmotic pressure & interstitial hydrostatic pressure – Causes inward movement of fluid. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 26. Increased vascular permeability is due to :- • Reduced osmotic pressure in the vasculature • Increased osmotic pressure in the interstitium www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 28. • Short – lived. (15-30 min.) • Reversible process. • For e.g. Mild thermal injury www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 29. •Endothelial cell contraction occurs rapidly after binding of mediators to specific receptors , is called the immediate transient response. •A slower and more prolonged contraction of endothelial cells, resulting from changes in the cytoskeleton, may be induced by cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1). •This reaction may take 4 to 6 hours to develop after the initial trigger and persist for 24 hours or more. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 30. • It is usually seen after severe injuries (burns and some infections). www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 31. In most cases leakage begins immediately after the injury and persists for several hours (or days) therefore, this reaction is known as the immediate sustained response. Venules, capillaries, and arterioles can all be affected, depending on the site of the injury. Direct injury to endothelial cells may also induce a delayed prolonged leakage that begins after a delay of 2 to 12 hours, lasts for several hours or even days, and involves venules and capillaries. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 32. • Accumulated leucocytes release toxic oxygen species & proteolytic enzymes. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 33. CELLULAR EVENTS -The cellular phase of inflammation consists of 2 processes: 1) Exudation of leucocytes. 2) Phagocytosis. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 34. The sequence of extravasation of Leukocytes from blood to tissues: Margination and pavementing Adhesion and Rolling Emigration and Diapedesis Chemotaxis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 35. Exudation of leukocytes Changes in the formed elements of blood Margination: Due of stasis of blood flow, leukocytes assumes a more peripheral position along the endothelial surface because of loss of plasma by exudation and it is called as margination. Pavementing: The neutrophils rests and adheres to the endothelium resembling pebbles and it is known as pavementing. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 38. • Rolling and adhesion: Pavemented neutrophils slowly rolls over the endothelial cell lining the vessel wall this is followed by firm adhesion. 4 type of distinct adhesion molecule: Selectins Addresins Integrins Immunoglobulin super family adhesion molecule www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 40. Emigration After adhesion, neutrophils throw out their cytoplasmic pseudopods. It gets lodged between endothelial cells and basement membrane. Damages basement membrame with secreted collagenases. Escapes out into extravascular space. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 42. CHEMOTAXIS The Chemotactic factors mediate transmigration of leukocytes to reach interstitial tissue. The factors are: Leukotriene B4 Platelet factor 4 Complement system Cytokines Soluble Bacterial products MCP-1 Chemotactic factor for CD4 +T cells & eosinophils. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 43. The concept of chemotaxis is well illustrated by Boyden’s chamber experiment. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 44. Phagocytosis : “Phagocytosis is defined as the process of engulfment of solid particulate material by the cells(cell-eating)”. Steps in phagocytosis: 1. Attachment stage 2. Engulfment stage 3. Secretion (Degranulation stage) 4. Killing/ Degradation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 45. Stages in phagocytosis: 1) Attachment or opsonisation: In order to establish a bond between microorganism and phagocytic cell ,the microorganism gets coated with opsonins. And their corresponding receptor is present on the phagocyte. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 46. The two main opsonins present in the serum and their corresponding receptor on the surface of phagocytic cell are: 1) IgG opsonin : Its receptor on Fc fragment of immunoglobulin on surface of phagocytic cell. 2)C3b opsonin : Is a fragment of complement and corresponding receptor for C3b on the surface of phagocytic cells. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 47. 2) ENGULFMENT STAGE: The opsonised particle is engulfed by formation of cytoplasmic pseudopods around the particle, enveloping it in phagocytic vacuole. The lysosome of the cell fuses with the phagocytic vacuole and forms phagolysosome. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 48. 3) DEGRANULATION: PMNs discharge granules into phagosomes and extracellular environment. Primary granules (azurophilic granules) fused with phagosomes. Secondary granules are discharged. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 49. 4) KILLING OR DEGRADATION STAGE: The microorganism after being killed by anti bacterial substance are degraded by hydrolytic enzymes. The antimicrobial agent acts by the following mechanism : 1) Oxygen dependent bacterial mechanism. 2) Oxygen independent bacterial mechanism. 3) Nitric oxide mechanism. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 52. Stages of phagocytosis of a foreign particle www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 54. Presented by: Sadaf Alvi Guided by: Dr. Minal Chaudhary Dr. Madhuri Gawande Dr.Swati patil Dr. Alka Hande www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 55. Learning objectives: At the end of the seminar learner should be able to: 1. Describe inflammatory mediators. 2. Describe outcomes, morphological patterns of inflammation. 3. Describe the clinical importance of inflammation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 56. CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 57. Cell-derived mediators CELL- DERIVED Mast cells, basophils, platelets Platelets Inflammatory cells Histamine Serotonin •PGs •Leukotriens •PAF •Cytokines •Nitric oxide & o2 metabolite Permeability & vasodilatation Permeability & vasodilatation Vasodilatation .fever, pain Permeability, chemotaxis, ,leukocytic adhesion Fever , pain Tissue damage www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 59. 1. VASOACTIVE AMINES: Two important pharmacologically active amines that have role in the early inflammatory response , they are so named as they have important action on blood vessels . They are: A.HISTAMINE. B.SEROTONIN (5- HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE). www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 60. Histamine: It is stored in the granules of mast cells, basophils and platelets. Various factors responsible for the release of it : Stimuli or substances inducing acute inflammation e.g. heat, cold, irradiation, trauma, irritant chemicals. Anaphylatoxins like fragments of complement C3a , and C5a, Histamine-releasing ptoteins from leukocytes. Neuropeptides such as substance P. Interleukins IL-1 IL-8. It causes:- • Vasodilatation of arterioles. Increased vascular permeability of venules , itching and pain. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 61. Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine) It is present in tissues like chromaffin cells of GIT, spleen, nervous tissue, mast cells and platelets. . Actions :- increased vascular permeability vasodilatation . www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 62. Arachidonic acid metabolites (eicosanoids ) Arachidonic acid is a 20 carbon Polyunsaturated fatty acid derived from dietary sources or by conversion from the essential fatty acid linoleic acid. • It is present in esterified form as a component of cell membrane phospholipids. • It is released from membrane phospholipids through the action of cellular phospholipases. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 65. 3. LYSOSOMAL COMPONENTS Neutrophils and monocytes contain lysosomal granules, which when released, may contribute to the inflammatory response. These are as under: 1. Granules of neutrophils Specific/ Secondary. Azurophil/ Primary. 2. Granules of monocytes and tissue macrophages & eosinophils. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 66. • Large azurophil ( primary) granules contains myeloperoxidase, bactericidal factors ( lysozymes, defensins), acid hydrolases & variety of neutral proteases. •Different granule enzyme serves different functions acid proteases act within the cell to cause destruction of bacteria and neutral proteases attack on extra cellular components. • Smaller specific ( secondary) granules contains lysozyme, collagenase, gelatinase, lactoferrin, plasminogen activator, histamine & alkaline phosphatase. a. Granules of neutrophills: www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 67. b. Granules of monocytes and tissue macrophages: • Releases mediators of inflammation like acid proteases, collagenase and plasminogen activator. • More active in chronic inflammation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 68. Eosinophil granule proteins Following activation by an immune stimulus, eosinophils degranulate to release an array of cytotoxic granules that are capable of inducing tissue damage and dysfunction. These include: •Major basic protien (MBP) •Eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) •Eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) •Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) c. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 69. 4. Platelet-Activating Factor Generated from membrane phospholipids of neutrophils, monocytes, basophils, mast cells, endothelium and platelets. Actions: vasoconstriction . Bronchoconstriction. Increased vascular permeability. Enhanced leukocyte adhesion. Chemotaxis and Degranulation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 70. 5. CYTOKINES • Cytokines are polypeptide substances produced by activated lymphocytes and activated monocytes. • TNF and IL-1, IL-6 are major cytokines that mediate inflammation . • Action in inflammation: • 1) Local effects: • Endothelium • Leukocytes • Fibroblasts • 2)Systemic effects www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 71. Chemokines are proteins that act primarily as chemoattractants to specific types of leukocytes. They are classified into four major groups :- C-X-C Chemokine: Act primarily on neutrophils. C-C Chemokine : chemotactic for all leukocytes except neutrophils. C Chemokine: specific for leukocytes. CX3C Chemokine: Act on monocyte and T-cells. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 72. 6. NITRIC OXIDE Nitric oxide (NO) is described as vascular relaxation factor produced by endothelial cells, macrophages and neurons in the brain. Various functions of NO :- Vasodilatation. Anti-platelet activating agent. Microbicidal action. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 73. 7. OXYGEN DERIVED FREE RADICAL They are released extracellularly from neutrophils and macrophages after exposure to microbes and include superoxide oxygen (0‘2), H202, OH' . These oxygen-derived free radicals have the following action in inflammation: Endothelial cell damage and thereby increased vascular permeability. Activation of protease and inactivation of antiproteases causing tissue matrix damage. Damage to other cells like RBC. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 75. Plasma derived mediators PLASMA- DERIVED FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM KININ SYSTEM COMPLEMENT SYSTEM Fibrin split products Kinin/ Bradykinin Anaphylotoxins C3a, C4a, C5a permeability Permeability, pain Permeability ,chemotaxis www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 76. A. Kinin system ◦ The kinins are vasoactive peptides derived from plasma protein (kininogens) by the action of specific proteases called Kallikreins. ◦ Bradykinin is the most important Kinin . www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 77. ACTIVATION OF KININ SYSTEM ACTIVATION OF KININ SYSTEM www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 79. Functions of Bradykinin: - Increases vascular permeability. - Causes contraction of smooth muscle. - Vasodilatation. - Pain www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 80. • This system is activated by plasminogen activator. • The sources of which include kallikrein of the kinin system, endothelial cells and leucocytes. • Plasminogen activator acts on plasminogen present as component of plasma proteins to form plasmin. • Further breakdown of fibrin by plasmin forms fibrinopeptides or fibrin split products . B.FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 82. The actions of plasmin in inflammation are: •Splits off complement C3 to form C3a which is a permeability factor. • fibrin split products which increase vascular permeability and are chemotactic to leucocytes. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 83. C. COMPLEMENT SYSTEM It is a cascade system of enzymatic proteins. function in both innate and adaptive immunity. consists of more than 20 proteins. complement proteins are present in inactive forms in the plasma . many of them are activated to become proteolytic enzymes that degrade other complement proteins. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 84. The critical step in complement activation is proteolyis of C3. Cleavage of C3 occurs by one of the three pathways: 1. Classical pathway 2. Alternative pathway 3. Lectin pathway www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 85. The activation and functions of the complement system. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 86. The biologic functions of complement system fall into 3 general categories 1) Inflammation – C5a,C3a and C4a(lesser extent) 2) Phagocytosis-C3b acts as opsonins and promote phagocytosis. 3) Cell lysis - deposition of MAC(membrane attack complex)makes cells permeable to water and ions results in cell death. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 87. Vasodilatation Prostaglandins Nitric oxide Histamine Serotonin, Increased vascular permeability Vasoactive amines C3a and C5a Bradykinin Leukotrienes PAF Substance P Chemotaxis C5a Leukotriene B4 Chemokines Fever IL-1, TNF Prostaglandins Pain Prostaglandins Bradykinin, substance p Tissue damage Neutrophil and macrophage lysosomal enzymes Oxygen metabolites Nitric oxide Role of Mediators in Different Reactions of Inflammation www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 88. Outcomes of acute Inflammation Complete resolution. Healing by connective tissue replacement (fibrosis). Progression to chronic inflammation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 89. Outcomes of Acute Inflammationwww.indiandentalacademy.com
- 90. MORPHOLOGIC PATTERNS OF INFLAMMATION 1. Serous inflammation. 2. Fibrinous inflammation 3. Suppurative or Purulent inflammation (Abscess formation) 4. Ulcers www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 97. SYSTEMIC EFFECTS OF ACUTE INFLAMMATION Fever - Occurs due to bacteraemia. - In response to infection various chemical mediators releases like prostaglandins, interleukin-1, TNF are released. •Leucocytosis Neutrophilia points to bacterialinfection. Lymphocytosis points to viral infection. Eosinophilia points to allergy or parasitic infection. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 98. Lymphangitis- Lymphadenitis: • Manifestation of localized inflammatory injury. • The lymphatics and lymph nodes that drain the inflamed tissue show reactive inflammatory changes in the form of lymphangitis and lymphadenitis. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 99. Benign (reactive) lymphadenopathy There are three distinct patterns of benign lymphadenopathy: •Follicular hyperplasia - Seen in infections, autoimmune disorders. •Paracortical hyperplasia - Seen in viral infections, skin diseases. •Sinus histiocytosis - Seen in inflammatory lesions and malignancies. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 100. Shock: • Occur in severe cases. • Massive release of cytokine TNF- alpha in response to severe tissue injury or infection results in profuse systemic vasodilatation, increased vascular permeability and intravascular volume loss. •The net effect of these changes is hypotension and shock. www.indiandentalacademy.com
- 101. CONCLUSION: The survival of all organism requires that they should eliminate foreign invaders such as, infectious pathogens and damaged tissues. These functions are mediated by a complex host response called inflammation. Inflammation accomplishes its protective mission by, destroying or otherwise neutralizing harmful agents. The body attempts to heal the damage with some changes by the process of repair. The repair begins almost as soon as the inflammatory changes have started and involves several processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation. www.indiandentalacademy.com
